Currently, companies are increasingly implementing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) solutions to improve operations and customer satisfaction.
Every ERP project is unique in nature and it requires a detailed approach that comes into play and proves to be helpful in the later stages of the project and sometimes even post Go-Live.
A well-designed implementation plan and monitoring is the key to success.
Key Factors Of The Successful ERP Implementation:
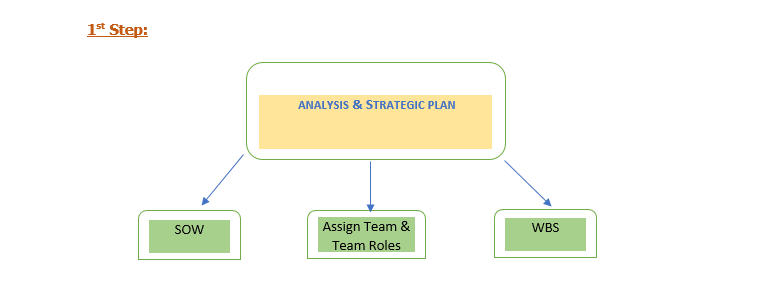
Scope of Work (SOW):
The first step in the ERP implementation should begin with defining the Scope of Work(SOW) of the project. SOW should contain project work details and expected outcomes of a project, mitigating any miscommunication between the Client & the project team.
Assign Team & Team Roles:
For an efficient implementation, the dedicated project team makes this job much easier.
Each team member should be committed to the success of the project and accountable for specific tasks, i.e. developing a timeline, finalizing objectives, unit testing, formulating a training plan.
Project Core Team members can be:
- Project Manager
- Project Lead
- Solution Consultant
- Developer
- Tester
- Single Point of Contact (SPC) form Customer End
- Application Testing Team from Customer End
To ensure that the implementation goes in the right direction for all the departments (Sales, Purchase, Production, QCA, Inventory and Account & Finance) Client needs to define the Steering Committee.
In the Steering Committee following members can be involved :
- Management – For project analysis
- HOD(s) – For sharing the department wise status
- Project Manager – For sharing the project status, upcoming plan & risks, if any
- Customer Project SPC – To verify the project status
Work Breakdown Structure (WBS):
The project team should create a work breakdown structure in which the scope of work, project goals, timelines, and individual team member roles & responsibilities should be defined
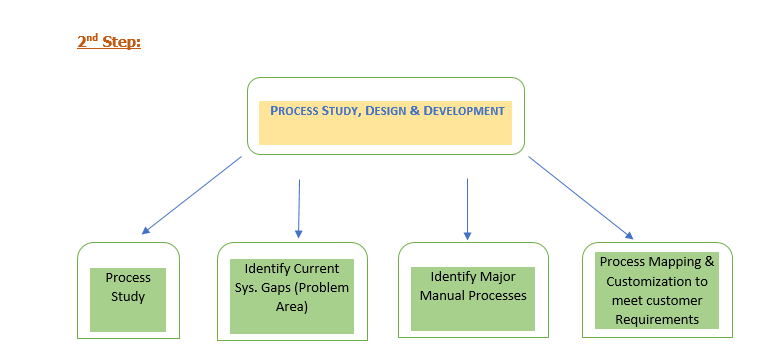
Process Study:
By using the project scope of work, the implementation team will do the detailed customer process study.
And project team must create Functional Requirement Document(FRD) and map As IS process with To-Be process.
Gap-Analysis document which will not get mapped in the standard system.
Identify Gaps:
Gap identification is very important so that both the client and implementation team sit together and try to find an alternative solution for whatever gap has been identified. Also, gap identification help to mitigate the miscommunication between the customer & implementation team for the respective process against which gap has been identified.
Identify Major Manual Processes:
Both the teams (Implementation & customer) must evaluate which processes are currently running manually and how to incorporate them & automate in the ERP.
Process Mapping & Customization to meet the customer Business Processes :
- Identify the processes and map with the right function and setups
- Solution Consultant should prepare the technical development document to fulfill the customer requirements
- The development team should work as per the technical development document and complete the development & first level testing within the defined timeline as per the WBS
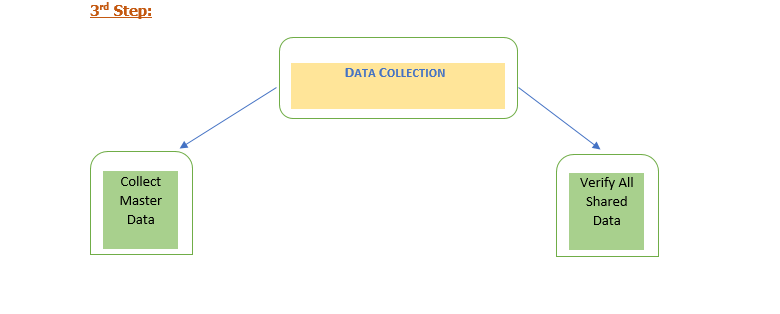
Collect Required Data:
Implementation team have to analyse the required data based on the defined business processes and can create a simple format of excel to collect the master data from the Customer.
Verify All Shared Data:
After collecting all the data from the client, the Implementation team have to verify all the shared data. It is very important as master data drives an ERP.
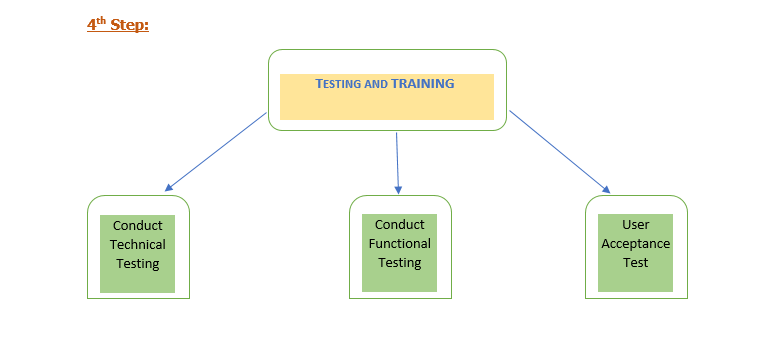
Conduct Technical Testing:
The project development team should test the developed functionality in the test database to confirm that all the validations and data type is accurate and working correctly.
The development team should maintain a development version control document.
Conduct Functional Testing:
The project functional team will have to ensure all the process-wise functionality running as per the business requirement.
Also, real-business scenarios should be used for validating the accuracy of the output.
User Acceptance Test:
The project team conducts the UAT at the client’s premises. The project team and client should set up user workstations for at least seven days of training by the functional team.
In this phase involvement of key users is highly required, who have depth knowledge of their business processes for testing. Key Users should pre-plan the test cases/checklist that they might want to run to confirm the functionality.
Go-live Check List:
A project team can create a Go-Live Checklist, For Example:
- Production Server Setup
- DB setup
- Remote Connection
- Physical Inventory process – From Client-side
- Opening Balances entry – New Database / Data Migration
- Opening Balances entries verification
- On-Site assistance to users for a week
- Database Backup Plan
Post Go-live Support:
One of the major risk factors of an unsuccessful ERP implementation is post-Go-Live support.
Both the team should understand, a successful ERP implementation is the start of a journey, it’s not a destination.
The implementation partner can deliver this by creating a dedicated help desk team.
In addition, a post-implementation audit should be performed after the system has been live to ensure all the transactions are happening in the right way.
It is very important to periodically review the system’s performance to maximize ROI.
Brief Statement:
- Set SOW & Goals
- Make a detailed project plan/ WBS
- Project Control and Monitoring
- Make project implementation team accountable for the ERP implementation
- Don’t go with huge customizations
- Train the Trainee Concept
- Post-Go-Live Support
Write To US For A FREE Demo At marketing@prudencesoftech.com

